Hash&KMP
Hash
哈希表
哈希冲突
1. 开散列法
在遇到$hash$值相同的不同$key$值时,通过邻接表存储所有$key$值.
- 优点: 实现简单方便
- 缺点: 在使用时,需要根据情况动态开空间
2. 闭散列法
在遇到$hash$值相同的不同$key$值时,向后寻找未被使用的$hash$值,存入$key$值
- 优点: 在使用过程中,不需要再开更多空间
- 缺点: 实现较为麻烦
思路: 开一个set,记录雪花出现情况,枚举同一个雪花的不同形态,在set查询。若没找到,再插入当前雪花,时间复杂度$O(12nlogn)$,(使用unordered_set时间复杂度为$O(12n)$但常熟较大且实现困难,使用set更好)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
struct Node
{
int a[6]{};
bool operator<(const Node &o) const
{
for (int i=0;i<6;i++)
{
if (a[i]!=o.a[i])
{
return a[i]<o.a[i];
}
}
return false;
}
bool operator==(const Node &o) const
{
for (int i=0;i<6;i++)
{
if (a[i]!=o.a[i])
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
set<Node> st;
Node get(Node &s,int i,int d)
{
Node res;
for (int &j:res.a)
{
j=s.a[i];
i+=d;
i=(i+6)%6;
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
int n;
cin>>n;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
Node s;
for (int &j:s.a)
{
cin>>j;
}
for (int j=0;j<6;j++)
{
if (st.find(get(s,j,1))!=st.end()||st.find(get(s,j,-1))!=st.end())
{
cout<<"Twin snowflakes found.";
return 0;
}
}
st.insert(s);
}
cout<<"No two snowflakes are alike.";
return 0;
}
树哈希
注意OIWiki上的三种树$hash$方法全是错的,都已经被Hack。
正确的树$hash$:
- 子树按$hash$值排序 + 括号序字符串$hash$合并
思路: 计算2颗数的$hash$,判断是否相同,时间复杂度$O(nlogn)$
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
char tree[3005];
ull base[3005];
int ed;
pair<ull,int> getHash()
{
ull hsh=1;
vector<pair<ull,int>>vec;
while (tree[++ed]=='0')
{
vec.push_back(getHash());
}
sort(vec.begin(),vec.end());
int x=1;
int sz=2;
for (auto p:vec)
{
sz+=p.second;
hsh=hsh*base[x]+p.first;
x=p.second;
}
hsh=hsh*3+2;
return make_pair(hsh,sz);
}
int main()
{
base[0]=1;
for (int i=1;i<=3000;i++)
{
base[i]=base[i-1]*3;
}
int n;
cin>>n;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
memset(tree,'1',sizeof tree);
tree[0]='0';
cin>>(tree+1);
ed=0;
ull hsh=getHash().first;
memset(tree,'1',sizeof tree);
tree[0]='0';
cin>>(tree+1);
ed=0;
ull hash1=getHash().first;
if (hsh==hash1)
{
cout<<"same\n";
}
else
{
cout<<"different\n";
}
}
return 0;
}
思路: 先计算出$G$和$H$的每个子树的$hash$,对于树$G$中的一个节点$u_1$找到一个在$H$中对应的点$u_2$,将$u_2$ 的所有孩子为根的子树的$hash$值放入一个集合$U$中.枚举$u_1$的每个孩子$v$,若$U$中包含以$v$为根的树的$hash$值,则删去,若$U$中不包含,放入$U0$.若操作结束后$U$中元素比$U0$多,则无解。否则,尝试让$U0$与$U$中元素两两配对,对于$U0$ 中无法配对的元素,全部删去,配对后再递归执行上述比较。对于$U0$中元素个数$>k$的情况,则要么需要删去的点的数量$>k$,要么不可能达到目标,一定无解。否则,因为$k\leq5$则可以直接枚举每种匹配情况,最多$k!$种情况。
树$hash$时间复杂度$O(nlogn)$,执行上述匹配,时间复杂度$O(nk!)$,总时间复杂度$O(nk!)$
代码:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
int fa[2][500005];
vector<int> adj[2][500005];
ull base[1000005];
ull hsh[2][500005];
int siz[2][500005];
int root[2];
int n[2];
int k;
void read(int kk)
{
cin>>n[kk];
for (int i=1;i<=n[kk];i++)
{
cin>>fa[kk][i];
if (fa[kk][i]!=-1)
{
adj[kk][fa[kk][i]].push_back(i);
}
else
{
root[kk]=i;
}
}
}
void getHash(int kk,int u)
{
hsh[kk][u]=1;
siz[kk][u]=1;
vector<pair<ull,int>> vec;
for (int v:adj[kk][u])
{
getHash(kk,v);
vec.emplace_back(hsh[kk][v],siz[kk][v]);
siz[kk][u]+=siz[kk][v];
}
sort(vec.begin(),vec.end());
for (auto p:vec)
{
hsh[kk][u]=hsh[kk][u]*base[p.second<<1]+p.first;
}
hsh[kk][u]=hsh[kk][u]*3+2;
}
pair<bool,int> compare(int u1,int u2,int mxk)
{
if (hsh[0][u1]==hsh[1][u2])
{
return make_pair(true,0);
}
if (siz[0][u1]<=siz[1][u2]||adj[0][u1].size()<adj[1][u2].size())
{
return make_pair(false,0);
}
multimap<ull,int>mp;
vector<int> vec;
for (int v:adj[1][u2])
{
mp.emplace(hsh[1][v],v);
}
for (int v:adj[0][u1])
{
auto it=mp.find(hsh[0][v]);
if (it!=mp.end())
{
mp.erase(it);
}
else
{
vec.push_back(v);
}
}
if (vec.size()>mxk)
{
return make_pair(false,0);
}
vector<int> vec1;
for (auto &p:mp)
{
vec1.push_back(p.second);
}
sort(vec.begin(),vec.end());
sort(vec1.begin(),vec1.end());
int ans=1e9;
do
{
int cnt=0;
bool flag=false;
for (int i=0;i<vec1.size();i++)
{
auto p=compare(vec[i],vec1[i],mxk-cnt);
if (!p.first)
{
flag=true;
break;
}
else
{
cnt+=p.second;
}
}
if (flag)
{
continue;
}
for (int i=(int)vec1.size();i<(int)vec.size();i++)
{
cnt+=siz[0][vec[i]];
}
ans=min(ans,cnt);
}
while (next_permutation(vec.begin(),vec.end()));
return make_pair(ans<=mxk,ans);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
cout.tie(nullptr);
base[0]=1;
for (int i=1;i<=1000000;i++)
{
base[i]=base[i-1]*3;
}
int C,T;
cin>>C>>T>>k;
while (T--)
{
read(0);
read(1);
getHash(0,root[0]);
getHash(1,root[1]);
auto p=compare(root[0],root[1],k);
cout<<(p.first?"Yes\n":"No\n");
//clear
for (int i=0;i<=max(n[0],n[1]);i++)
{
siz[1][i]=siz[0][i]=hsh[0][i]=hsh[1][i]=fa[0][i]=fa[1][i]=0;
adj[0][i].clear();
adj[1][i].clear();
}
}
return 0;
}
更多资料:
字符串Hash
使用 unsigned long long自然溢出,或者双模数。
可以使用二分 + $Hash$的方法快速比较两个字符串的字典序。
思路: $hash_r-hash_{l-1}*base^{len}$快速计算区间$hash$值,时间复杂度$O(n+m)$
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
char s[1000005];
ull hsh[1000005];
ull base[1000005];
int n;
ull getHash(int l,int r)
{
int len=r-l+1;
return hsh[r]-hsh[l-1]*base[len];
}
int main()
{
cin>>(s+1);
n=strlen(s+1);
base[0]=1;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
hsh[i]=hsh[i-1]*27+s[i]-'a'+1;
base[i]=base[i-1]*27;
}
int m;
cin>>m;
while (m--)
{
int l1,r1,l2,r2;
cin>>l1>>r1>>l2>>r2;
cout<<(getHash(l1,r1)==getHash(l2,r2)?"Yes\n":"No\n");
}
return 0;
}
思路: 枚举回文中点,二分查找此中点能形成的最长回文串,使用$hash$进行check,时间复杂度$O(nlogn)$
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
ull hsh[2][1000005];
ull base[1000005]={1};
int n,ans;
ull getHash(int x,int l,int r)
{
int len=abs(r-l)+1;
return hsh[x][r]-hsh[x][l+(x?1:-1)]*base[len];
}
bool check(int x,int y)
{
bool a1=getHash(0,x+1,x+y)==getHash(1,x-1,x-y);
bool a2=getHash(0,x+1,x+y)==getHash(1,x,x-y+1);
if (a1)
{
ans=max(ans,y<<1|1);
}
if (a2)
{
ans=max(ans,y<<1);
}
return a1||a2;
}
int find(int x)
{
int ans=0;
int l=1,r=min(x,n-x);
while (l<=r)
{
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if (check(x,mid))
{
l=mid+1;
ans=max(ans,mid);
}
else
{
r=mid-1;
}
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int T=0;
for (int i=1;i<=1000000;i++)
{
base[i]=base[i-1]*27;
}
while (++T)
{
string x;
cin>>x;
n=x.length();
if (x=="END")
{
return 0;
}
ans=1;
memset(hsh[0],0,sizeof hsh[0]);
memset(hsh[1],0,sizeof hsh[1]);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
hsh[0][i]=hsh[0][i-1]*27+x[i-1]-'a'+1;
}
for (int i=n;i>=1;i--)
{
hsh[1][i]=hsh[1][i+1]*27+x[i-1]-'a'+1;
}
for (int i=1;i<x.length();i++)
{
find(i);
}
cout<<"Case "<<T<<": "<<ans<<"\n";
}
return 0;
}
思路: 枚举每个后缀,通过二分$hash$求出与$B$的的重复长度,之后$O(1)$回答询问,时间复杂度$O(nlogn)$
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
ull base[200005]={1};
int ans[200005];
ull hsh[2][200005];
string a,b;
int n,m;
bool check(int x,int y)
{
return hsh[0][x+y-1]-hsh[0][x-1]*base[y]==hsh[1][y];
}
int find(int x)
{
int l=0,r=min(n-x+1,m);
int res=0;
while (l<=r)
{
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
if (check(x,mid))
{
l=mid+1;
res=mid;
}
else
{
r=mid-1;
}
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
for (int i=1;i<=200000;i++)
{
base[i]=base[i-1]*27;
}
int q;
cin>>n>>m>>q>>a>>b;
for (int i=1;i<=max(n,m);i++)
{
if (i<=n)
{
hsh[0][i]=hsh[0][i-1]*27+a[i-1];
}
if (i<=m)
{
hsh[1][i]=hsh[1][i-1]*27+b[i-1];
}
}
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
ans[find(i)]++;
}
while (q--)
{
int x;
cin>>x;
cout<<ans[x]<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
KMP
思路: 一个字符串$S$的最短循环节长度应是$|S|-|border|$($S$长度减去$border$长度),并且循环节长度需要$|S|$的因数.
证明: 一个字符串$S$的最短循环节长度应是$|S|-|border|$
$S[1 ~ (|S|-某个匹配的前后缀的长度)]$一定是一个循环节
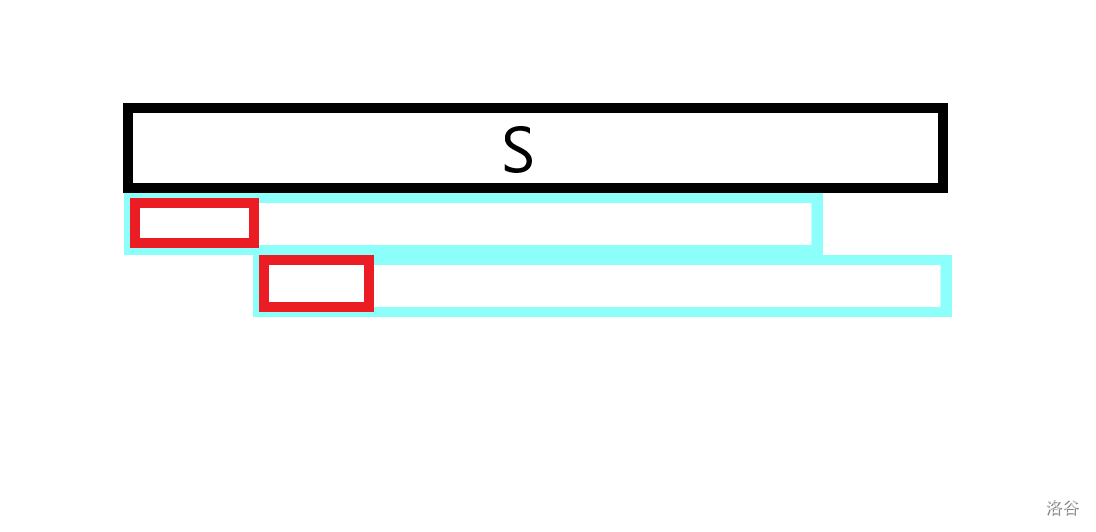
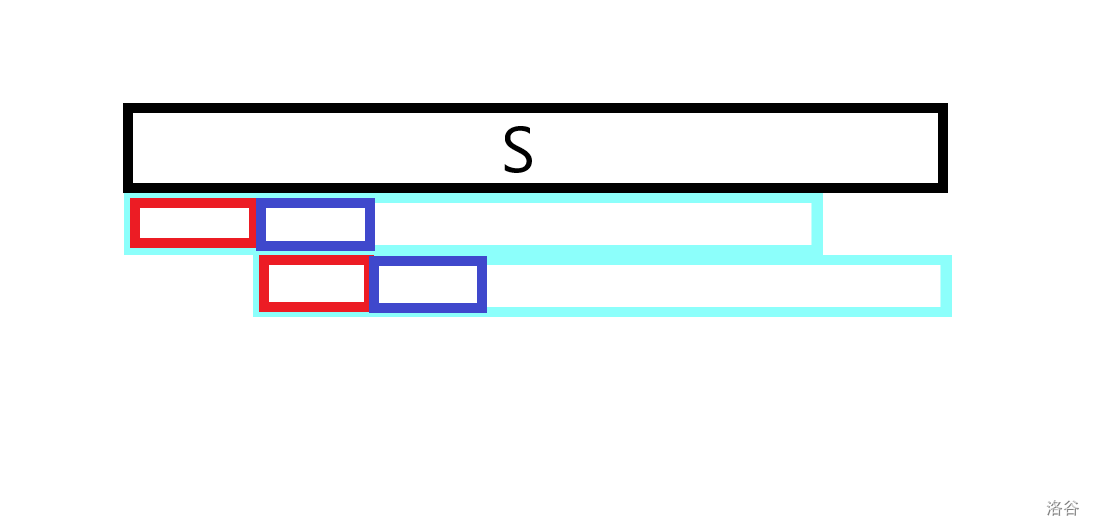
如图,假设匹配的前后缀是蓝色部分,红色部分则是循环节,因为两个蓝色部分相等,则后缀中的红色部分等于前缀中的红色部分
显然,前缀中的深蓝部分等于后缀中的红色部分,而后缀中的深蓝部分等于前缀中的深蓝部分,以此类推,可以证明
第2段(深蓝色)等于第1段(红色),第3段等于第2段(深蓝色)…直到结束,所以$S[1 ~ (|S|-某个匹配的前后缀的长度)]$一定是一个循环节循环节一定是$S[1 ~ (|S|-某个匹配的前后缀的长度)]$
设循环次数为$K$,则第
1 ~ (K-1)个循环节应与第2~K个循环节相同,则1 ~ (K-1)为匹配的前缀,2 ~ K为后缀匹配的前后缀越长,
|S|-其长度越小,即循环节最小。因为$border$是最长的匹配的前后缀,所以$|S|-|border|$是最短循环节为什么不可能是$border$的$border$:因为$border$是最长的前后缀,所以$1$中的红色部分是最短的循环节,若不是,例如红色部分是由
2个更小的循环节组成,则前后缀长度可以增长更小循环节的长度,不满足$border$的定义。而循环节只能是由若干个最短循环节组成的(否则,它们长度的最大公因数也将会是循环节,这就找到了更小循环节),所以若最短的循环节都不是$|S|$的因数,则其他循环节一定不是。而找$border$的$border$找到的循环节一定不会比最短循环节短
时间复杂度$O(n)$
代码:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
int n;
string s;
int nxt[1000005];
void getNext()
{
nxt[1]=0;
for (int i=2,j=0;i<=n;i++)
{
while (j>0&&s[i]!=s[j+1])
{
j=nxt[j];
}
if (s[i]==s[j+1])
{
j++;
}
nxt[i]=j;
}
}
int main()
{
int T=0;
while ((cin>>n)&&n)
{
cin>>s;
s=' '+s;
T++;
cout<<"Test case #"<<T<<'\n';
getNext();
for (int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
if (i%(i-nxt[i])==0&&nxt[i]!=0)
{
cout<<i<<' '<<i/(i-nxt[i])<<'\n';
}
}
cout<<'\n';
}
return 0;
}
思路: 枚举覆盖子矩阵的宽度,对于一个宽度$d$,可以将整个区间切成若干个$R*d$的矩阵,通过$hash$ 快速判断这些矩阵是否相同。若相同,再在竖直方向上,依据横向的$hash$值做$kmp$匹配,求出循环节,时间复杂度$O(CR+C^2)$
代码:
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
int n,m;
string s[80];
ull base[10005]={1};
ull hsh[2][10005][80];
int nxt[10005];
void getNext(int x)
{
nxt[1]=0;
for (int i=2,j=0;i<=n;i++)
{
while (j>0&&hsh[0][i][x]!=hsh[0][j+1][x])
{
j=nxt[j];
}
if (hsh[0][i][x]==hsh[0][j+1][x])
{
j++;
}
nxt[i]=j;
}
}
void getHash()
{
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for (int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
hsh[0][i][j]=hsh[0][i][j-1]*27+s[j][i]-'A'+1;
}
}
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for (int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
hsh[1][i][j]=hsh[1][i-1][j]*27+s[j][i]-'A'+1;
}
}
}
int main()
{
for (int i=1;i<10000;i++)
{
base[i]=base[i-1]*27;
}
cin>>n>>m;
for (int i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
for (int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
if (!i)
{
s[j]+=' ';
continue;
}
char ch;
cin>>ch;
s[j]+=ch;
}
}
int ans=1e9;
getHash();
for (int d=1;d<=m;d++)
{
bool flag=false;
for (int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
if (hsh[1][n][(i-1)%d+1]!=hsh[1][n][i])
{
flag=true;
break;
}
}
if (flag)
{
continue;
}
getNext(d);
ans=min(ans,d*(n-nxt[n]));
}
cout<<ans<<'\n';
return 0;
}
最小表示法
思路: 求出$2$个字符串的最小表示,然后判断$2$个字符串的最小表示是否相同,时间复杂度$O(n)$
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned __int128 uint128;
string a,b;
int get(string &xx)
{
string x=' '+xx+xx;
int n=xx.length();
int i=1,j=2,k;
while (i<=n&&j<=n)
{
for (k=0;k<n&&x[i+k]==x[j+k];k++);
if (k==n)
{
break;
}
if (x[i+k]>x[j+k])
{
i=i+k+1;
if (i==j)
{
i++;
}
}
else
{
j=j+k+1;
if (i==j)
{
j++;
}
}
}
return min(i,j);
}
int main()
{
cin>>a>>b;
int x=get(a)-1;
int y=get(b)-1;
string res="Yes\n";
for (int i=0;i<a.length();i++)
{
if (a[(x+i)%a.length()]!=b[(y+i)%b.length()])
{
cout<<"No";
return 0;
}
res+=a[(x+i)%a.length()];
}
cout<<res;
return 0;
}